-
QR CODES -
PRODUCT FREE
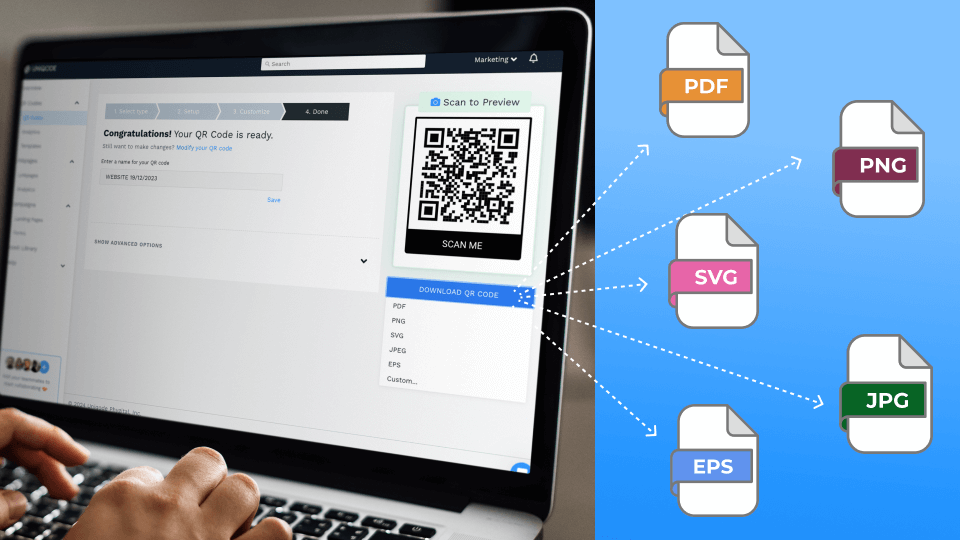
QR Code Generator
Create custom QR Codes for every use case
-
Dynamic QR Code Generator
-
Choosing the Best QR Code Generator
-
QR Code Tracking
-
QR Code API
-
GET STARTED
Select a template to continue
-
-
DIGITAL BUSINESS CARDS
-
PRODUCT POPULAR
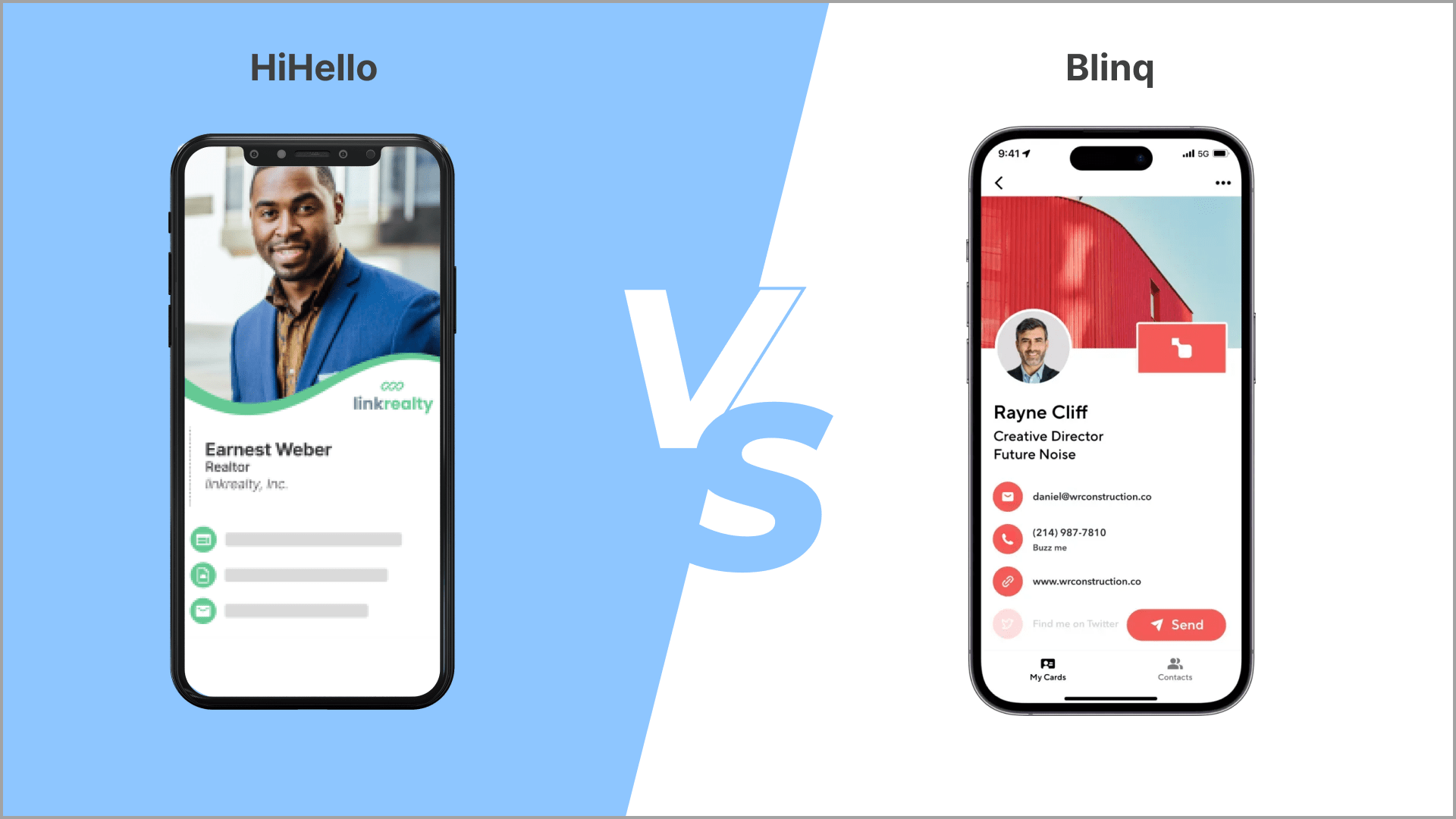
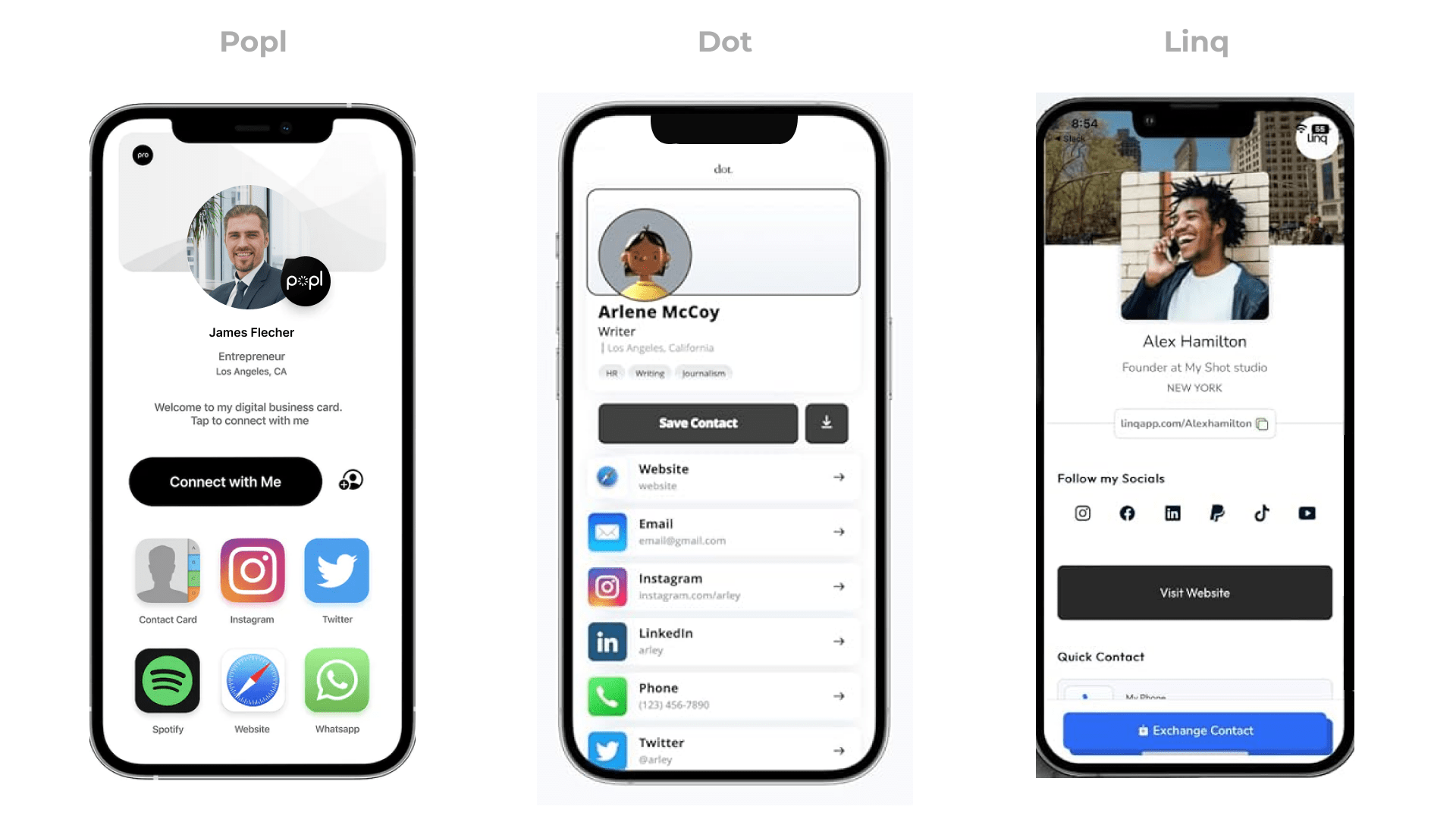
Digital Business Cards
Measure your networking with digital business cards
-
All About Digital Business Cards
-
Apple Wallet Business Cards
-
Physical Vs Digital Business Cards
-
Choosing The Best Digital Business Card Solution
-
GET STARTED
Select a template to continue
-
-
SOLUTIONS
-
LEARN
-
A powerful and easy solution for our business.
Uniqode’s solution has made our lives a lot easier.

MARCELO YANEZ
PRODUCT MANAGER,
NESTLE
Read all customer stories
-
PRICING
-
DEMO